The SemQL Language
SemQL is a language to express declarative rules in Semarchy xDM. It is used for example to define:
-
Enrichers, Matchers, Validations and Survivorship Rules involved in the Certification Process.
-
Composite and transformed attributes in form and collections appearing in the applications.
-
Filters when browsing data in the Data Hub.
Main Characteristics
It has the following main characteristics:
-
The syntax is close to the SQL language and most SemQL functions map to Database functions.
-
SemQL is converted on the fly and executed by the data hub database.
-
SemQL uses Qualified Attribute Names instead of columns names. This makes the SemQL code independent from the underlying implementation.
SQL-Like Clauses
The SemQL language allows users to define SQL-Like clauses. Depending on the context, these clauses may be one of the following:
-
Condition: A clause that returns a boolean result from the evaluation of expressions using operators. A condition can be used for example for filtering or validating data records (if the clause is false, then the record is filtered out or considered invalid).
-
Expression: A clause that returns a value. In the context of a SemQL Enricher for example, an expression transforms, standardizes and enriches source attributes.
-
Order By Clause: An expression used to sort records. In consolidation rules, such a clause is used to manage the consolidation conflicts. For example, consider a consolidation made by Most Frequent Value. When multiple values occur with equal frequency, then the SemQL in the Ranking Expression determines which value is used.
| SemQL is used to create expressions, conditions and order by clauses. SELECT, UPDATE or INSERT queries are not supported, as well as joins, sub-queries, aggregates, in-line views and set operators. |
| Users proficient with SQL should not be mistaken by the appearances. Even if SemQL looks like SQL, the SemQL expressions are entirely parsed and rewritten by the Semarchy xDM platform into SQL before their execution by the hub database. A simple SemQL expression may result into a complex SQL statement. As a consequence, it is not recommended to try injecting SQL statements within SemQL expressions. |
Attribute, Variables and parameters
SemQL clauses manipulate attributes, variables and parameters defined in objects of the Semarchy xDM model.
For example:
-
The
firstNameattribute of thecustomerentity. -
The
productFamilyNameparameter of thesearchProductByFamilysearch form.
Attributes are accessed through an unambiguous Qualified Attribute Name. The qualified attribute name is the path to an attribute from the entity being processed.
This path allow you to simply navigate the references that link entities of the model. For example, the manager.lastName would return the last name of the manager of an employee record.
Functions
You can use built-in functions in SemQL. Most of these functions map directly to functions of the hub’s database. Other functions (for example, matching functions) are specific to Semarchy xDM.
You can also use in SemQL customized functions implemented in the database.
The SemQL Editor
The SemQL Editor lists the attributes, variables, parameters as well as all built-in and customized SemQL functions with their syntax. It is used in the application builder to design SemQL expressions, conditions or clauses.
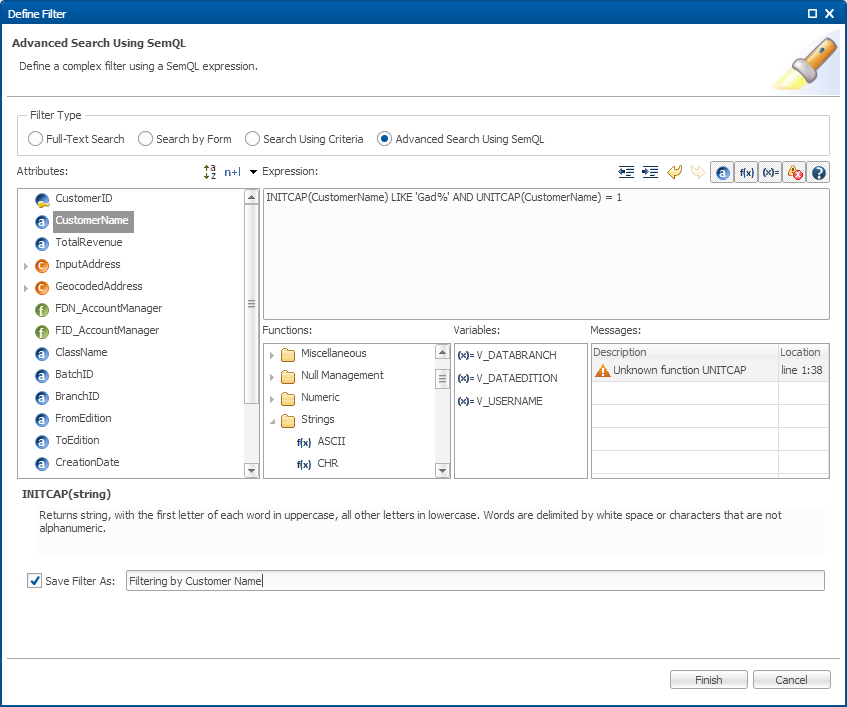
This editor is organized as follows:
-
Attributes available for the expression appear in left panel. Double-click an attribute to add it to the expression.
-
Functions declared in SemQL appear in the left bottom panel, grouped in function groups. Double-click a function to add it to the expression.
-
Variables available for the expression appear in the bottom center panel.
-
Messages appear in the right bottom panel, showing parsing errors and warnings.
-
Description for the selected function or attribute appear at the bottom of the editor.
-
The Toolbar allows to indent the code or hide/display the various panels of the editor and to undo/redo code edits.