| This is documentation for Semarchy xDI 2023.3, which is no longer supported. For more information, see our Global Support and Maintenance Policy. |
Getting Started with SAP
This article explains how to get started with the SAP Component.
Overview
The Semarchy xDI SAP Connector can use four types of SAP structures for integration:
-
Tables: Classic database tables storing SAP data.
-
IDocs: Documents.
-
BAPIs/RFCs: Services available to external systems for integration.
-
DataSources: Read-only structured data intended for reporting purposes.
Set Up the SAP Server
You must configure the SAP server to enable the connection from Semarchy xDI.
-
The Semarchy xDI custom ABAP must be deployed in the dedicated ZSTB_PACKAGE package and ZSTB_FUNCTION_GROUP function group.
-
The setup differs depending on the structure you will use for integration:
-
For tables, use ZSTB_RFC_READ_QUERY.
-
To manipulate IDocs, there is no RFC to run, but your must configure the network to enable access.
-
To call a BAPI/RFC, ensure it is remote enabled.
-
To query a DataSource, use ZSTB_RFC_READ_DATA_SOURCE.
-
Set Up the Designer
After setting up the SAP server, configure Semarchy xDI Designer:
-
Download the JCO libraries from the SAP website.
-
Copy and paste these libraries to the
c:/windows/system32and[DESIGNER_INTALLATION_FOLDER]/Contents/Eclipse/runtime/libdirectories.
The Designer is now ready for creating SAP metadata.
Create a SAP Metadata
To create a SAP metadata:
-
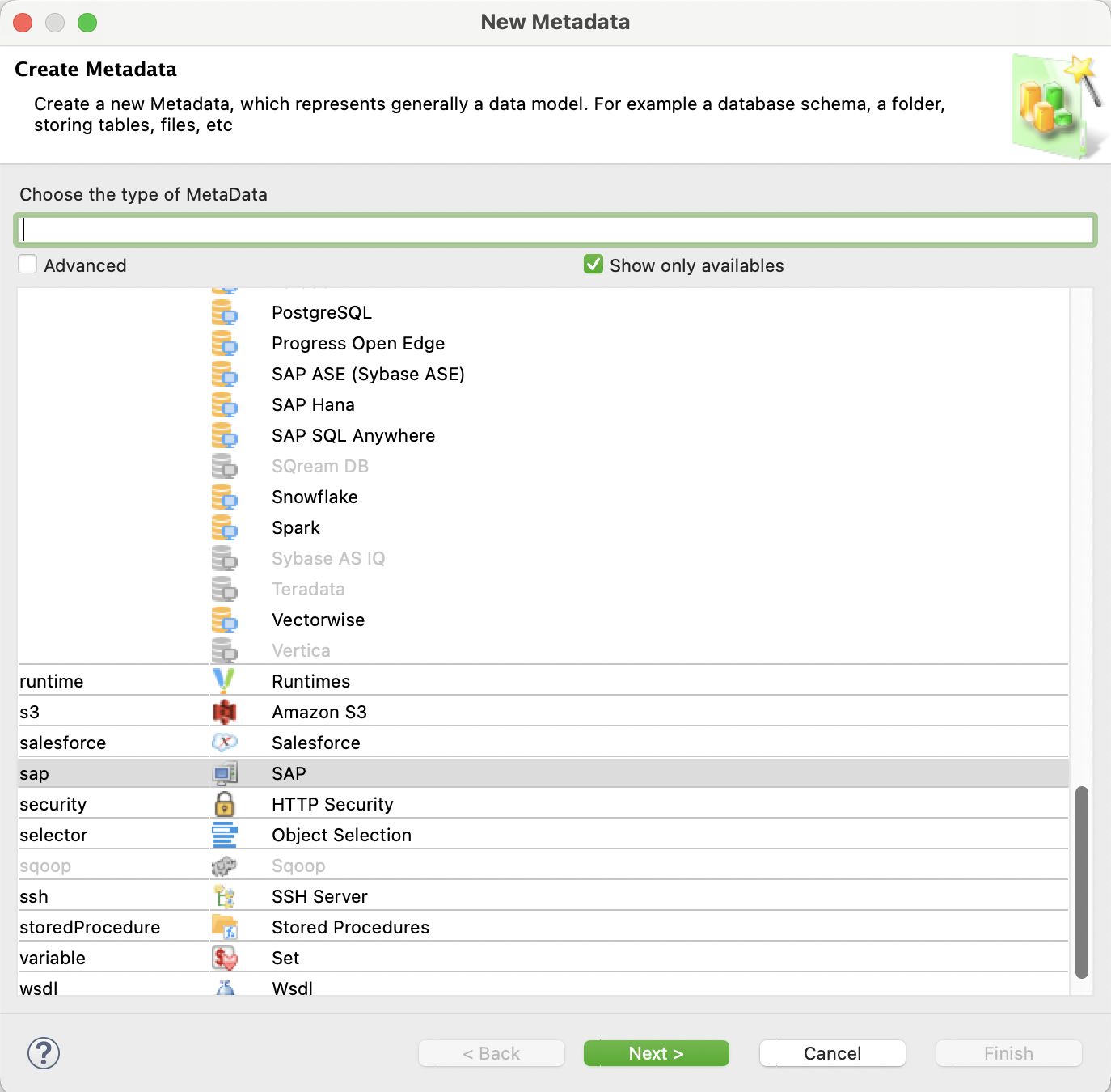
Right-click a folder in your project and then select New > Metadata.
-
In the New Metadata wizard, select SAP and then click Next.
-
Name the metadata and click Next.
-
Select the module and the third-party libraries required for the component and click Finish.
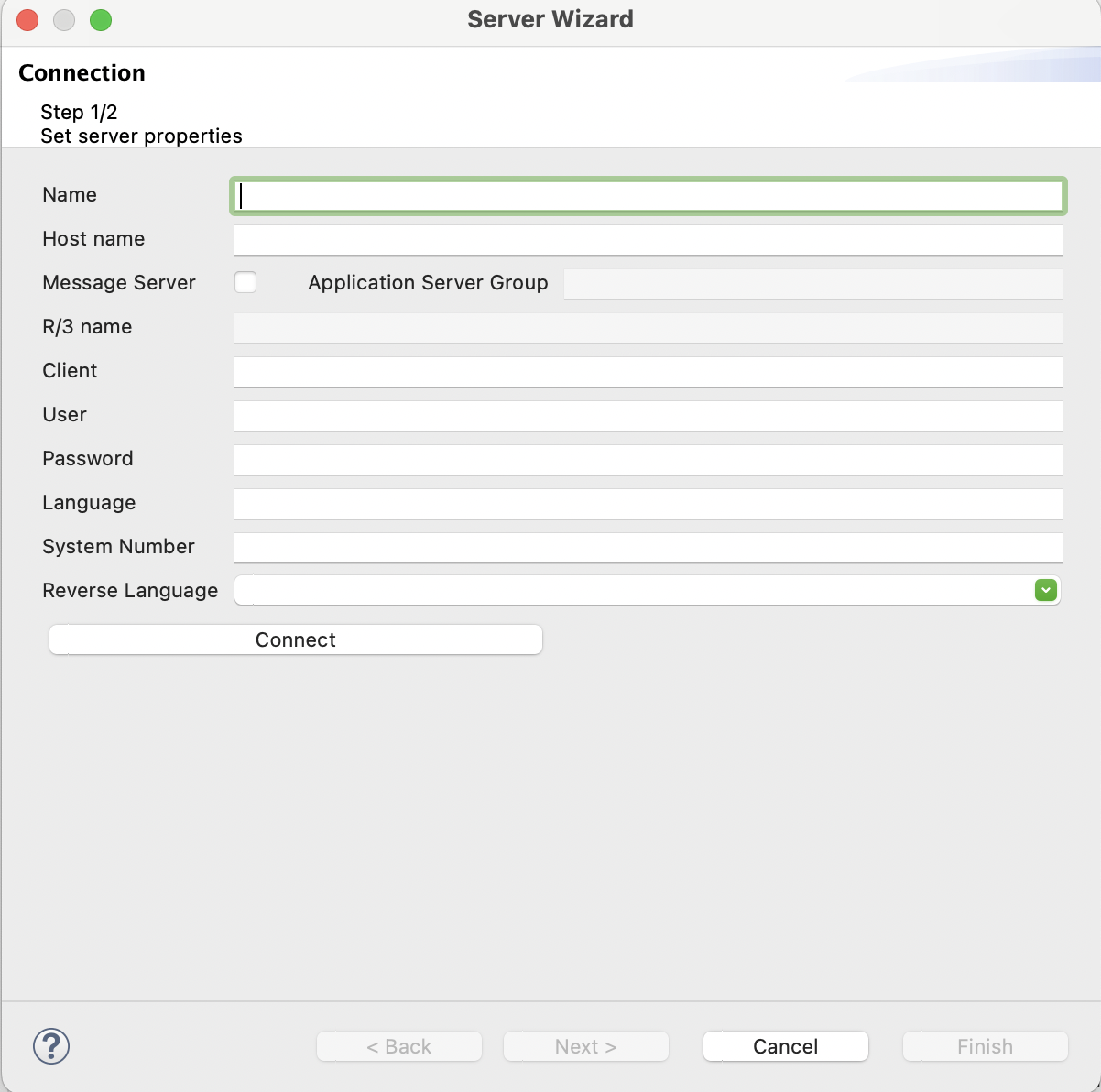
The metadata is created and the server wizard opens. -
In the server wizard, in the Connection page, enter the connection properties and click Next.
-
In the Reverse page, select the SAP objects that you want to reverse-engineer and click Finish.
The metadata is created.
SAP objects
The following sections details the SAP objects that can be reverse-engineered and used in Designer.
BAPI/RFC
In a BAPI/RFC metadata:
-
The inputs are under the ImportParameters node
-
The outputs are under the ExportStructures node.
-
Both inputs and outputs have a Tables node.
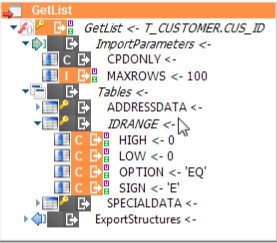
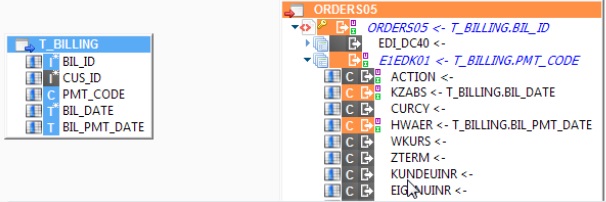
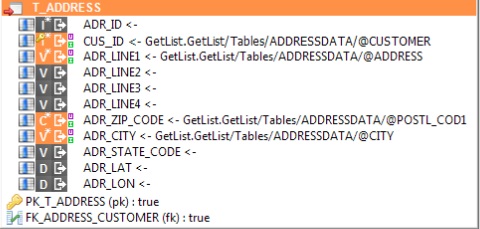
Tables
SAP tables are similar to plain database tables.
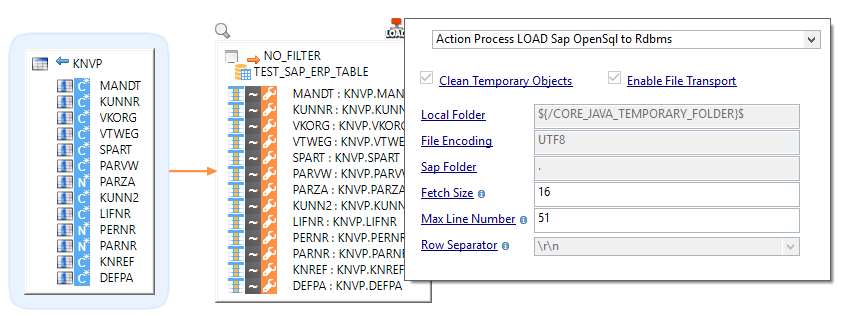
You can extract data from an SAP table in a regular mapping:
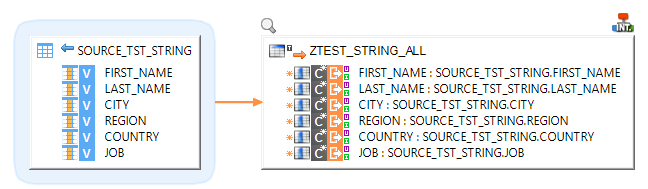
You can also integrate data into an SAP table:
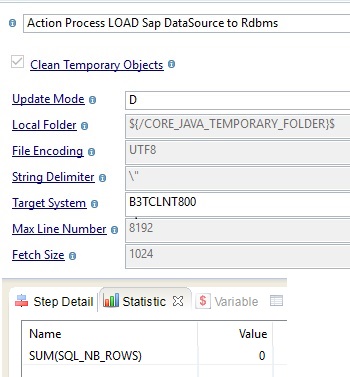
DataSources
An SAP DataSource is an extension of SAP Business Warehouse (BW). It is a set of fields that provide data for a business unit for reporting purposes. Datasources are read-only, structured data.
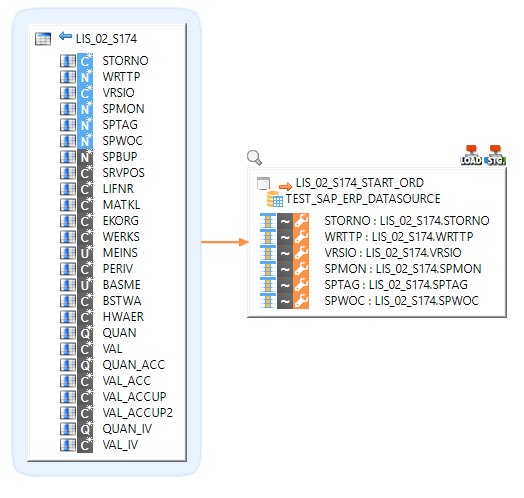
Datasources support a delta mode to only load changes. To use this mode, you must to first run a mapping with the Update Mode load template property set to C. This mode performs a full initial load and resets the counters.
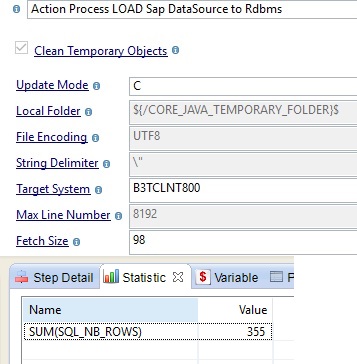
After the initial load, you can configure a delta load with the Update Mode set to D.