| This is documentation for Semarchy xDI 2024.1, which is no longer actively maintained. For more information, see our Global Support and Maintenance Policy. |
Getting started with JMS
Java Message Service (JMS) is a standard API for sending data messages between systems using a service bus. Follow this guide to get started with JMS in Semarchy xDI.
Create JMS metadata
Define JMS metadata
JMS metadata holds information about a JMS server, as well as its configured queues and topics. You can use this metadata in processes along with JMS actions to send and receive messages.
To create a JMS metadata object:
-
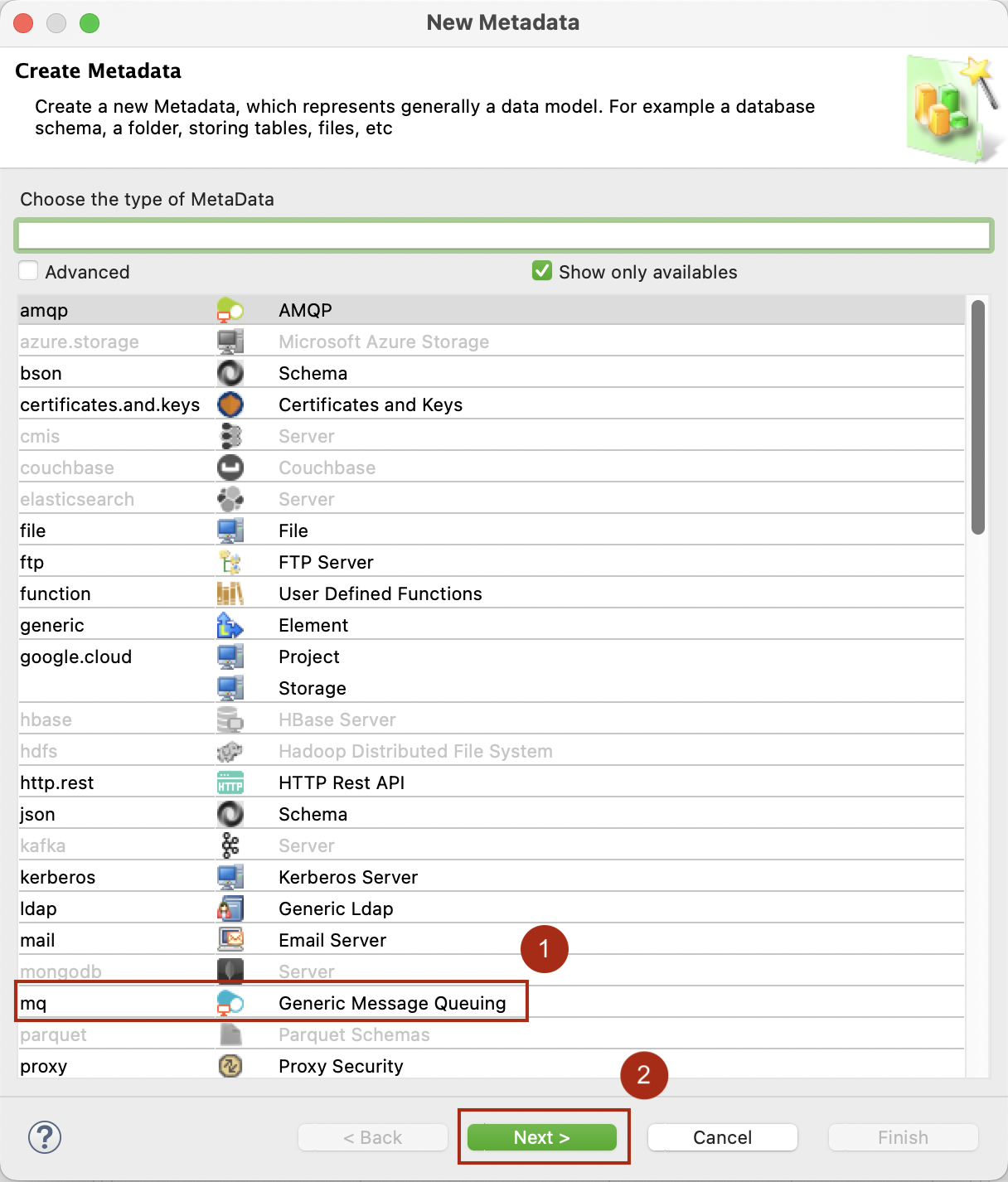
Right-click a folder in your project and then select New > Metadata.
-
In the New Metadata wizard, select Generic Message Queuing and then click Next.
-
Give the metadata object a name, and click Next.
-
Select the module and the third-party libraries required for the component and click Finish.
The metadata object is created. -
In this metadata object, select the server node, and complete the connection configuration. This configuration depends on your message bus. Common message bus configurations are as follows:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
Initial Context Factory Class |
|
Connection Factory Name |
|
URL |
|
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
Initial Context Factory Class |
|
Connection Factory Name |
|
URL |
|
| Property | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Initial Context Factory Class |
|
||
Connection Factory Name |
|
||
URL |
|
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
Initial Context Factory Class |
|
Connection Factory Name |
|
URL |
|
Define queues
Queues contain messages delivered to subscribers. Define queues after configuring the connection.
To define a queue:
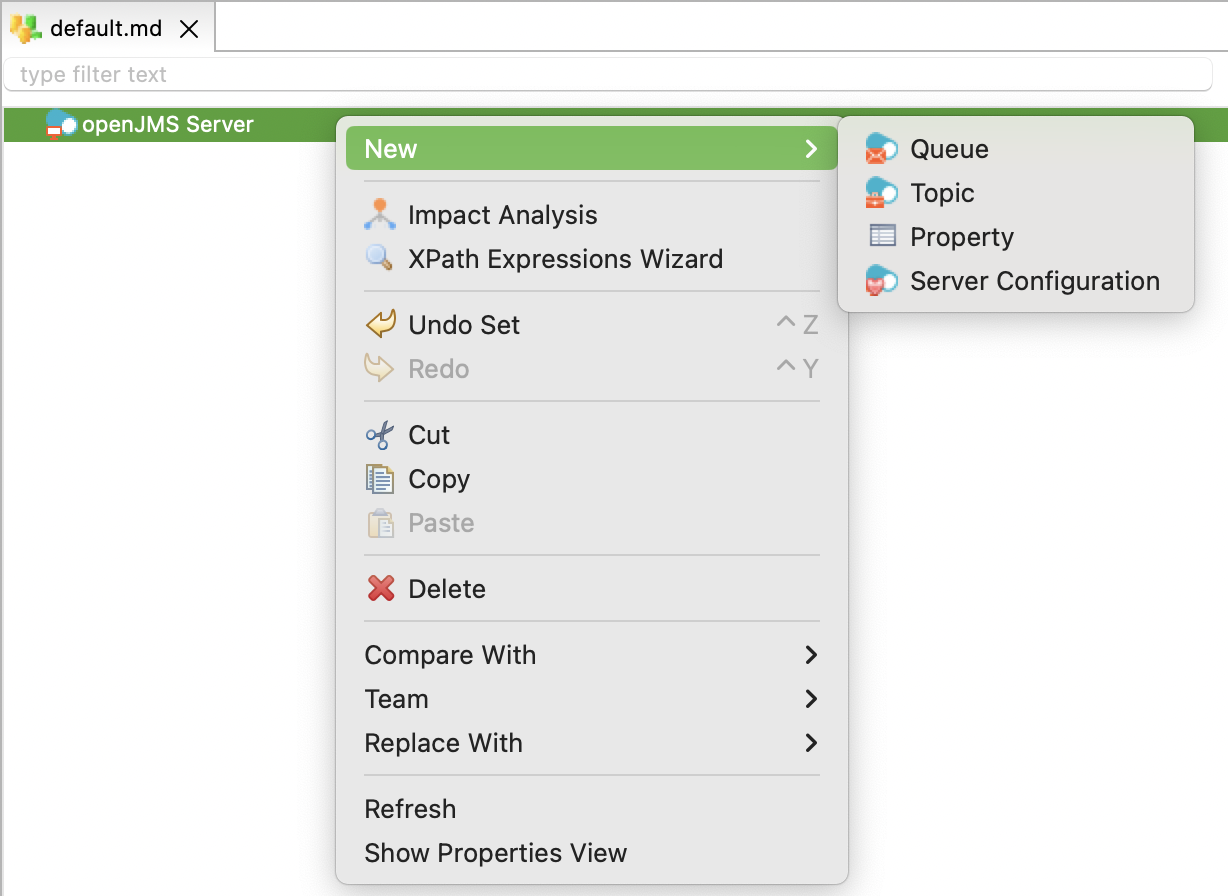
-
Right-click the server node and select New > Queue.
-
Enter a Name and a Physical Name for the queue.
For FFMQ, the physical name must be specified in the queue/<queue_name>format. For example,queue/Purchase_Queue -
If using Active MQ:
-
Right-click the server node and select New > Property.
-
In the new properties, set the Name
queue.<queue_name>and the Value to<queue_name>. -
Repeat the previous steps for each queue node, in such a way that the property node immediately follows the queue node.
-
| The Physical Name must match the name of the queue in the JMS server. Depending on their configuration, some JMS servers can create queues in real time. If this is not the case with your JMS server, make sure that queues you define in the metadata exist on the server. |
Define topics
Topics deliver messages using a publish and subscribe model. Multiple subscribers can subscribe to one topic.
To create a topic:
-
Right-click the server node and select New > Topic.

-
Enter a Name and a Physical Name for the topic.
For FFMQ, you must specify the physical name as topic/<topic_name>. For example,topic/Transactionsis a valid physical name. -
If using Active MQ:
-
Right-click the server node and select New > Property.
-
In the new property, set the Name to
topic.<topic_name>and the Value to<topic_name>. -
Repeat the previous steps for each topic node, in such a way that the property node immediately follows the topic node.
-
-
If you are using Active MQ, Open MQ, or FFMQ, set the JMS Client ID property on the server node. Multiple processes with the same JMS Client ID cannot run at the same time, and JMS uses this string property to distinguish different client applications. You can also set this property in JMS actions.
| The Physical Name must match the name of the topic in the JMS server. Depending on their configuration, some JMS servers can create topics in real time. If this is not the case with your JMS server, make sure that topics you define in the metadata exist in the server. |
Define subscribers
JMS subscribers consume message from a topic.
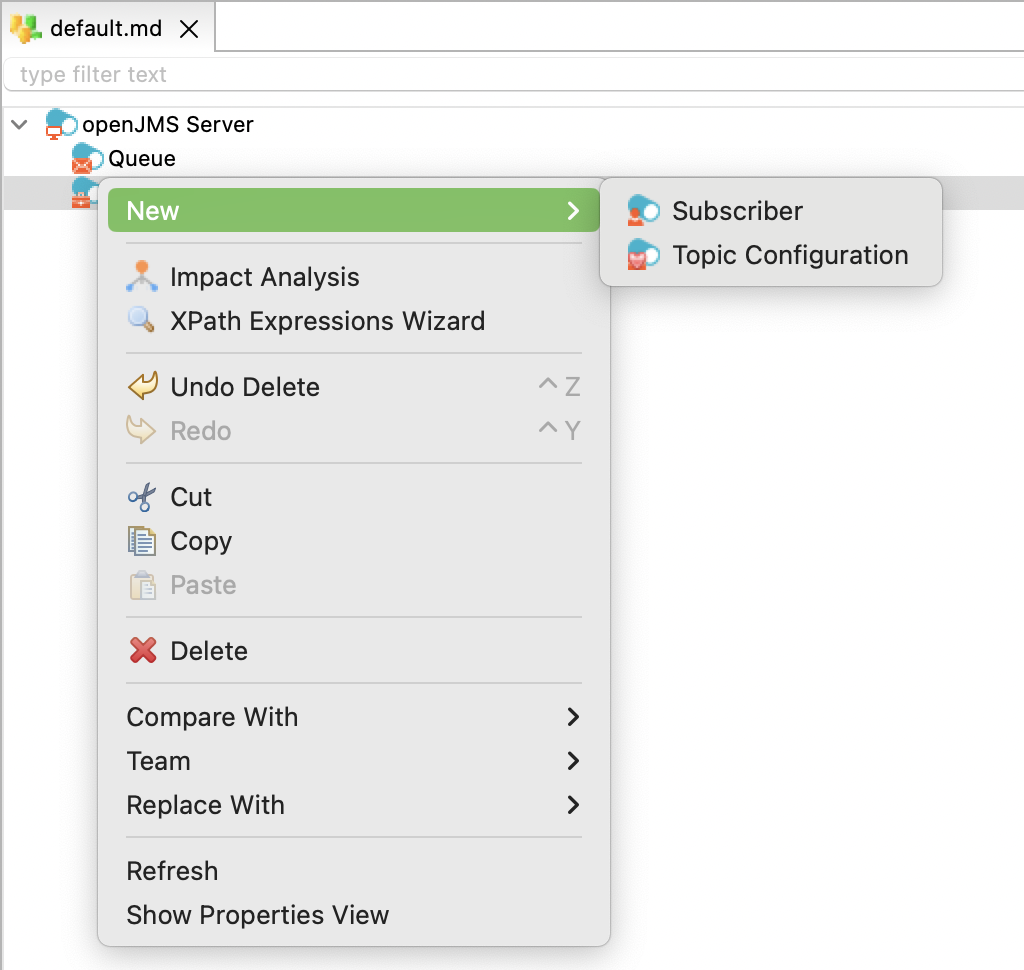
To create a subscriber:
-
Right-click the topic node and select New > Subscriber.
-
Enter the Name and the Physical Name of the subscriber.
| JMS servers automatically create subscribers when trying to read from a topic for the first time. Subscribers do not need to exist on the JMS server ahead of time. |
Use JMS in processes
The Process Palette in Semarchy xDI Designer lists actions in the Internet & Networking category to interact with JMS servers:
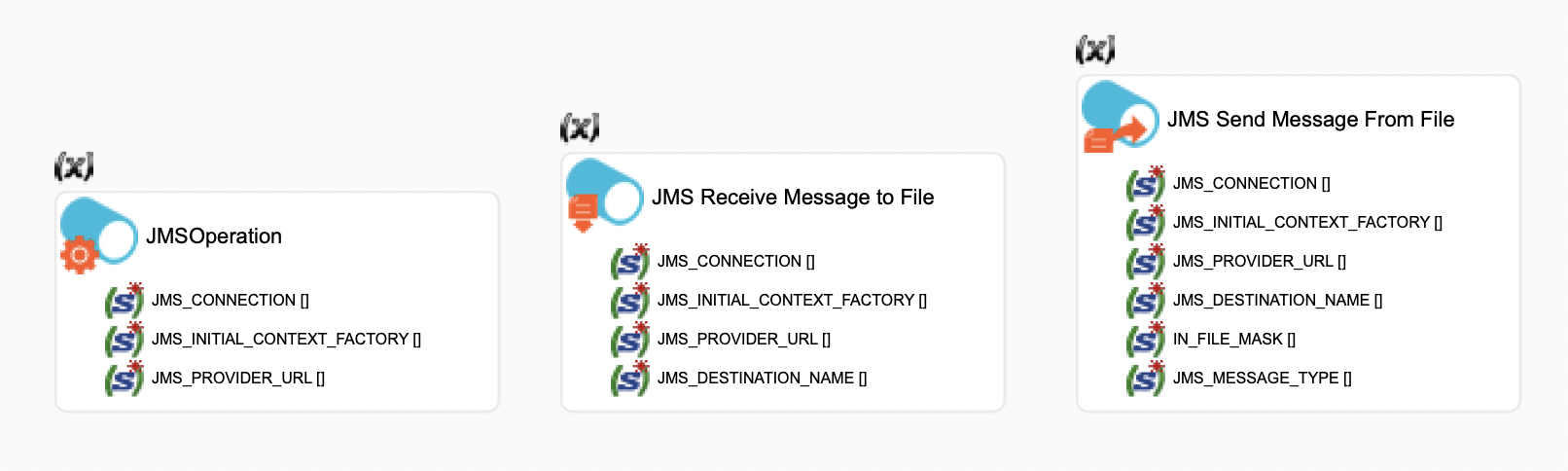
-
JMS Operation sends a JMS Operation to a remote JMS Server, such as commit or rollback.
-
JMS Receive Message to File receives messages from a JMS Server.
-
JMS Send Message From File sends a message to a JMS server.
The following tasks make use of these processes.
Send messages to a queue
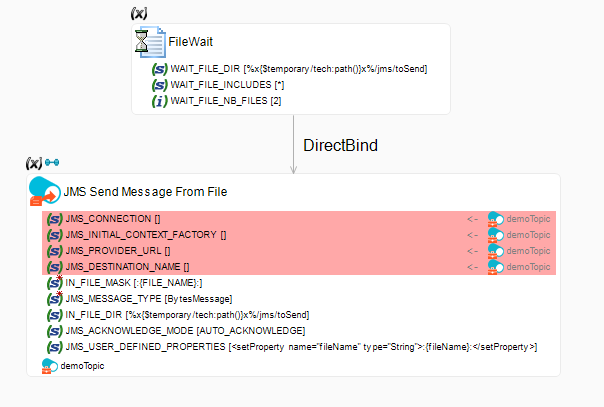
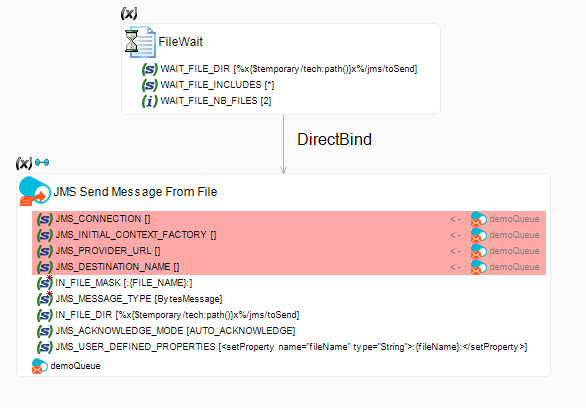
In the following example, the Send JMS File Message From File action sends a JMS message from files.
-
The File Wait action binds the files' parameters to the JMS action. A JMS message is sent for each file found by the File Wait action.
-
The corresponding queue node of the JMS metadata is dragged and dropped onto the JMS Send Message From File action to inherit properties from the metadata (JMS_CONNECTION, JMS_DESTINATION, and so on).
-
IN_FILE_MASKis the filename mask for the files to send as messages. It is set to:{FILE_NAME}:, which corresponds to the filename returned by the File Wait action through the bind link. -
JMS_MESSAGE_TYPEis set toByteMessage. -
IN_FILE_DIRis the directory containing the files, and matches the directory specified in the File Wait action. -
JMS_ACKNOWLEDGE_MODEis set toAUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE. The acknowledge mode determines how the consumer informs the provider that it has successfully received a message. -
JMS_USER_DEFINED_PROPERTIESdefines custom properties. It is set to<setProperty name="fileName" type="String">:{FILE_NAME}:</setProperty>.
With this configuration, thefileNameproperty is set to the name of the file. The message consumer may reuse this property to write it to a file with the same name.
-
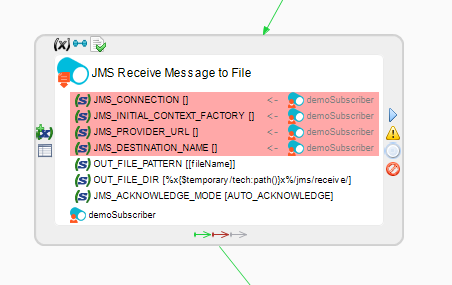
Consume messages from a queue
In the following example, the Receive JMS File Message to File action retrieves the message sent using the Send JMS File Message From File action from the previous section.
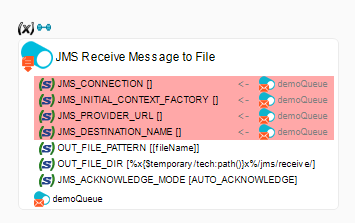
The corresponding queue node in the JMS metadata is dragged and dropped on Receive JMS File Message to File to set the connection properties.
The OUT_FILE_PATTERN parameter is set to [fileName], which corresponds to a JMS property. It is the same custom JMS property that was set in the JMS_USER_DEFINED_PROPERTIES parameter of the Send JMS File Message From File action. You can also set the OUT_FILE_PATTERN parameter in the same way.
|